Down syndrome
Updated: 2024-11-12
Overview
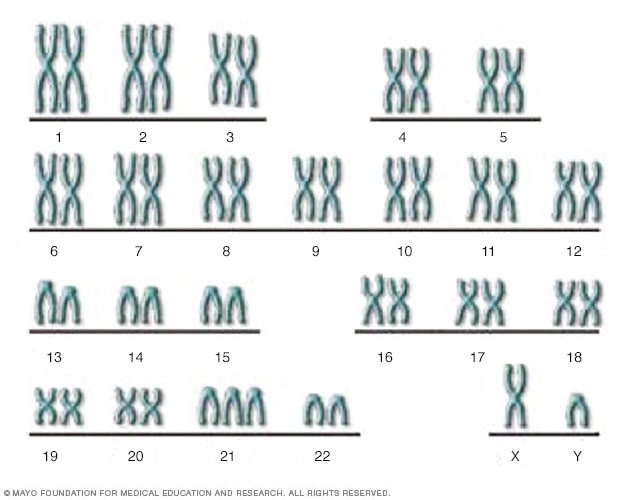
The genetic basis of Down syndrome
There are 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46. Half the chromosomes come from the egg and half come from the sperm. This XY chromosome pair includes the X chromosome from the egg and the Y chromosome from the sperm. In Down syndrome, there is an additional copy of chromosome 21, resulting in three copies instead of the usual two copies.
Down syndrome is a genetic condition caused when an unusual cell division results in an extra full or partial copy of chromosome 21. This extra genetic material causes the developmental changes and physical features of Down syndrome.
The term "syndrome" refers to a set of symptoms that tend to happen together. With a syndrome, there is a pattern of differences or problems. The condition is named after an English physician, John Langdon Down, who first described it.
Down syndrome varies in severity among individuals. The condition causes lifelong intellectual disability and developmental delays. It's the most common genetic chromosomal cause of intellectual disabilities in children. It also commonly causes other medical conditions, including heart and digestive system problems.
Better understanding of Down syndrome and early interventions can greatly improve the quality of life for children and adults with this condition and help them live fulfilling lives.
Symptoms
Each person with Down syndrome is an individual. Problems with intellect and development are usually mild to moderate. Some people are healthy while others have serious health issues such as heart problems that are present at birth.
Children and adults with Down syndrome have distinct face and body features. Though not all people with Down syndrome have the same features, some of the more common features include:
- Flattened face and small nose with a flat bridge.
- Small head.
- Short neck.
- Tongue that tends to stick out of the mouth.
- Upward slanting eyelids.
- Skin fold of the upper eyelid that covers the inner corner of the eye.
- Small, rounded ears.
- Wide, small hands with a single crease in the palm and short fingers.
- Small feet with a space between the first and second toes.
- Tiny white spots on the colored part of the eye called the iris. These white spots are called Brushfield's spots.
- Short height.
- Poor muscle tone in infancy.
- Joints that are loose and too flexible.
Infants with Down syndrome may be average size, but typically they grow slowly and remain shorter than other children the same age.
Developmental delays
Children with Down syndrome take longer to reach developmental milestones, such as sitting, talking and walking. Occupational therapy, physical therapy, and speech and language therapy can help improve physical functioning and speech.
Intellectual disabilities
Most children with Down syndrome have mild to moderate cognitive impairment. This means that they have problems with memory, learning new things, focusing and thinking, or making decisions that affect their everyday life. Language and speech are delayed.
Early intervention and special education services can help children and teens with Down syndrome reach their full potential. Services for adults with Down syndrome can help support living a full life.
When to see a doctor
Down syndrome usually is diagnosed before or at birth. But if you have any questions regarding your pregnancy or your child's growth and development, talk with your doctor or other healthcare professional.
Causes
Human cells usually contain 23 pairs of chromosomes. One chromosome in each pair comes from the sperm, the other from the egg.
Down syndrome results from an unusual cell division involving chromosome 21. This unusual cell division results in an extra partial or full chromosome 21. This extra genetic material changes how the body and brain develop. It is responsible for the physical features and developmental problems of Down syndrome.
Any one of three genetic changes can cause Down syndrome:
- Trisomy 21. About 95% of the time, Down syndrome is caused by trisomy 21. This means the person has three copies of chromosome 21, instead of the usual two copies. The extra chromosome 21 is in all cells in the body. Trisomy 21 results from an unusual cell division during the development of the sperm cell or the egg cell.
- Mosaic Down syndrome. This is a rare form of Down syndrome. People with mosaic Down syndrome have only some cells with an extra copy of chromosome 21. This mosaic of typical and changed cells is caused by an unusual cell division after the egg has been fertilized by the sperm.
- Translocation Down syndrome. In a small number of people, Down syndrome can occur when a part of chromosome 21 becomes attached, also called translocated, onto another chromosome. This can happen before or at conception. The person has the usual two copies of chromosome 21, but also has extra genetic material from chromosome 21 attached to another chromosome.
Is it inherited?
Most of the time, Down syndrome is not passed down in families. The condition is caused by a random unusual cell division. This can happen during the development of the sperm cell or the egg cell or during early development of the baby in the womb.
Translocation Down syndrome can be passed from parent to child. But only a small number of children with Down syndrome have translocation and only some of them inherited it from one of their parents.
Either parent may have a balanced translocation. The parent has some rearranged genetic material from chromosome 21 on another chromosome, but no extra genetic material. This means the parent has no signs of Down syndrome, but can pass an unbalanced translocation on to children, causing Down syndrome in the children.
Risk factors
Some parents have a greater risk of having a baby with Down syndrome. Risk factors include:
- Older age. Chances of giving birth to a child with Down syndrome goes up with age because older eggs have a greater risk of unusual chromosome division. The risk of having a child with Down syndrome increases after a pregnant person is 35 years of age. But most children with Down syndrome are born to pregnant people under age 35 because they have far more babies.
- Being carriers of the genetic translocation for Down syndrome. Either parent can pass the genetic translocation for Down syndrome on to their children.
- Having had one child with Down syndrome. Both parents who have one child with Down syndrome and parents who have a translocation themselves are at higher risk of having another child with Down syndrome. A genetic counselor can help parents understand the risk of having a second child with Down syndrome.
Complications
Health concerns that result from having Down syndrome can be mild, moderate or severe. Some children with Down syndrome are healthy, while others may have serious health problems. Some health concerns may become more of a problem as the person gets older.
Health concerns can include:
- Heart problems. About half the children with Down syndrome are born with some type of heart condition that is present at birth. These heart problems can be life-threatening and may require surgery in early infancy.
- Problems with the digestive system and digesting food. Stomach and intestinal conditions occur in some children with Down syndrome. These may include changes in the structure of the stomach and intestines. There is a higher risk of developing digestive problems, such as intestinal blockage, heartburn called gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or celiac disease.
- Problems with the immune system. Because of differences in their immune systems, people with Down syndrome are at higher risk of developing autoimmune disorders, some forms of cancer and infectious diseases such as pneumonia.
- Sleep apnea. Soft tissue and spinal changes can lead to blockage of the airways. Children and adults with Down syndrome are at greater risk of obstructive sleep apnea.
- Being overweight. People with Down syndrome are more likely to be overweight or obese compared with the general population.
- Spinal problems. In some people with Down syndrome, the top two vertebrae in the neck may not line up as they should. This is called atlantoaxial instability. The condition puts people at risk of serious injury to the spinal cord from activities that bend the neck too far. Some examples of these activities include contact sports and horseback riding.
- Leukemia. Young children with Down syndrome have a higher risk of leukemia.
- Alzheimer's disease. Having Down syndrome greatly raises the risk of developing Alzheimer's disease. Also, dementia often occurs at an earlier age than in the general population. Symptoms may begin around age 50.
- Other problems. Down syndrome also may also be linked with other health conditions, such as thyroid problems, dental problems, seizures, ear infections, and hearing and vision problems. Conditions such as depression, anxiety, autism and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) also may be more common.
Life expectancy
Over the years, there have been advances in healthcare for children and adults with Down syndrome. Because of these advances, children born today with Down syndrome are likely to live a longer life than in the past. People with Down syndrome can expect to live more than 60 years, depending on how severe their health problems are.
Prevention
There's no way to prevent Down syndrome. If you're at higher risk of having a child with Down syndrome or you already have one child with Down syndrome, you may want to talk with a genetic counselor before becoming pregnant.
A genetic counselor can help you understand your chances of having a child with Down syndrome. The counselor also can explain the prenatal tests that are available and help explain the pros and cons of testing.
Diagnosis
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends offering the option of screening tests and diagnostic tests for Down syndrome to all who are pregnant, no matter what age.
- Screening tests can suggest the likelihood or chances that you're carrying a baby with Down syndrome. But these tests can't tell for sure whether your baby has Down syndrome.
- Diagnostic tests can tell for sure whether your baby has Down syndrome.
Your healthcare professional can discuss the types of tests, advantages and disadvantages, benefits and risks, and the meaning of your results. If needed, your healthcare professional may recommend that you talk to a genetic counselor.
Screening tests during pregnancy
Screening for Down syndrome is offered as a routine part of care before the baby's birth, called prenatal care. Although screening tests can only tell your risk of carrying a baby with Down syndrome, they can help you make decisions about the need for diagnostic tests.
Screening tests include the first trimester combined test and the integrated screening test. The first trimester means about the first three months of pregnancy.
The first trimester combined test
The first trimester combined test is done in two steps. These include:
- Blood test. This blood test measures the levels of pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A) and the pregnancy hormone known as human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG). Levels of PAPP-A and HCG outside the standard range may indicate a problem with the baby.
- Nuchal translucency screening test. During this test, an ultrasound is used to measure a specific area on the back of your baby's neck. When certain conditions caused by chromosome changes are present, more fluid than usual tends to collect in this neck tissue.
Using your age and the results of the blood test and the ultrasound, your healthcare professional or genetic counselor can estimate the risk that your baby has Down syndrome.
Integrated screening test
The integrated screening test is done in two parts during the first and second trimesters of pregnancy. The results are combined to estimate the risk of your baby having Down syndrome.
- First trimester. Part one includes a blood test to measure PAPP-A and an ultrasound to measure nuchal translucency.
- Second trimester. The quad screen measures your blood level of four substances present in pregnancy: alpha fetoprotein, estriol, HCG and inhibin A.
Cell-free DNA testing
A small amount of DNA is released from the placenta into a pregnant person's bloodstream. This cell-free DNA in the blood can be examined for the extra chromosome 21 material of Down syndrome.
For those at risk of having an infant with Down syndrome, the test can be done starting at 10 weeks of pregnancy. If the test is positive, diagnostic testing is usually needed to confirm that the baby has Down syndrome.
Diagnostic tests during pregnancy
If your screening test results are positive or uncertain, or you're at high risk of having a baby with Down syndrome, you might consider more testing to confirm the diagnosis. Your healthcare professional can help you weigh the pros and cons of these tests.
Diagnostic tests that can identify Down syndrome include:
- Chorionic villus sampling (CVS). In CVS, cells are taken from the placenta. The cells are used to look at the baby's chromosomes. This test is usually done in the first trimester, between 10 and 14 weeks of pregnancy. The risk of pregnancy loss, called a miscarriage, from a CVS is very low.
- Amniocentesis. A sample of the amniotic fluid surrounding the baby in the womb is withdrawn through a needle inserted into the mother's uterus. This sample is then used to look at the chromosomes of the baby. This test is usually done in the second trimester, after 15 weeks of pregnancy. This test also carries a very low risk of miscarriage.
Couples who are being treated for infertility through in vitro fertilization (IVF) who know that they are at increased risk of passing on certain genetic conditions to their children may choose to have the embryo tested for genetic changes before it's implanted in the womb.
Diagnostic tests for newborns
A physical exam is usually enough to identify Down syndrome in an infant in the first 24 hours after birth. If your healthcare professional thinks that your infant has Down syndrome, your healthcare professional orders a test called a chromosomal karyotype to confirm the diagnosis. Using a sample of blood, this test looks at your child's chromosomes. If there's an extra full or partial chromosome 21 in all or some cells, the diagnosis is Down syndrome.
Treatment
Early intervention for infants and children with Down syndrome can make a major difference in improving their quality of life. Because each child with Down syndrome is unique, treatment will depend on your child's needs. Also, as your child gets older and enters different stages of life, your child may need different care or services.
For people with Down syndrome, ongoing services, including healthcare, education and life skills support, are important throughout life. Getting routine medical care and treating issues when needed can help keep a healthy lifestyle.
Team care
If your child has Down syndrome, you'll likely rely on a team of specialists that can provide medical care and help your child develop skills as fully as possible. Depending on your child's needs, your team may include some of these experts:
- Primary care pediatrician to coordinate and give routine childhood care.
- Pediatric heart specialist called a cardiologist.
- Pediatric digestive system specialist called a gastroenterologist.
- Pediatric specialist in treating hormone-related conditions called an endocrinologist.
- Developmental pediatrician.
- Pediatric nervous system specialist called a neurologist.
- Pediatric ear, nose and throat (ENT) specialist.
- Pediatric eye doctor called an ophthalmologist.
- Hearing professional called an audiologist.
- Speech and language therapist called a speech-language pathologist.
- Physical therapist.
- Occupational therapist.
You'll need to make important decisions about your child's treatment, services and education. Build a team of healthcare professionals, teachers and therapists you trust. These professionals can help find resources in your area and explain state and federal programs for children and adults with disabilities.
You may find it helpful to look for a developmental pediatrician, a specialist with expertise about Down syndrome. Also, some areas have a child Down syndrome specialty clinic that offers a range of services in one place. These experts give special attention to needs and issues that are more common in people with Down syndrome. They can work together with your primary care professional.
Adults with Down syndrome
As your child with Down syndrome becomes an adult, healthcare needs can change. Besides general health screenings recommended for all adults, ongoing healthcare includes evaluation and treatment for conditions that are more common in adults with Down syndrome. You may choose to visit an adult Down syndrome specialty clinic, if available.
Conditions common in adults with Down syndrome include:
- Vision and hearing problems.
- Dental issues.
- Low thyroid levels called hypothyroidism.
- Diabetes.
- Celiac disease and GERD.
- Heart disease, stroke and high cholesterol.
- Obesity.
- Sleep apnea.
- Mood and behavior changes.
- Alzheimer's disease.
- Bone problems, such as spine problems, arthritis and osteoporosis.
In addition to meeting health needs, caring for your adult loved one with Down syndrome includes planning for current and future life needs, such as:
- Living arrangements.
- Social and recreational opportunities.
- Support programs and jobs.
- Financial support.
- Guardianship.
Coping and support
When you learn your child has Down syndrome, you may experience a range of emotions. You may not know what to expect, and you may not be sure of your ability to care for a child with a disability. Information and support can help ease these concerns.
Consider these steps to prepare yourself and to care for your child:
- Ask your healthcare professional about early intervention programs in your area. Available in most states in the U.S., these special programs are for infants and young children with Down syndrome and other disabilities. They usually begin at birth until age 3. The programs help to develop motor, language, social and self-help skills. Most programs offer free screening to assess your child's abilities and needs. An Individual Family Service Plan (IFSP) is created to outline services to meet your child's needs.
- Learn about educational options for school. Depending on your child's needs, options may include attending regular classes, called mainstreaming, support staff in regular classes, special education classes, or a combination. An Individualized Education Plan (IEP) is a detailed, written document that describes how a school system will provide education that meets your child's needs. Talk to your school district about developing an IEP for your child.
- Seek out other families who have a family member with Down syndrome. Most communities and national organizations have support groups for parents and families of children and adults with Down syndrome. You also can find internet support groups. Family and friends can be a source of understanding and support too.
- Participate in social and leisure activities. Take time for family outings and look in your community for social activities such as park district programs, Special Olympics, sports teams or ballet classes. These kinds of activities can help your child feel part of a team and build self-confidence. Children and adults with Down syndrome can enjoy many social and leisure activities, though some adjustments may be needed to help them take part in activities.
- Encourage independence. Your child's abilities may be different from other children's abilities. But with your support and some practice, your child may be able to do independent tasks such as packing a lunch, bathing and dressing, cooking, house cleaning, and laundry. You might make a daily checklist of tasks to be done on your child's own. This will likely help your child feel more independent and accomplished.
- Prepare for the transition to adulthood. Opportunities for living, working, and social and leisure activities can be explored before your child leaves school. Community living or group homes and community employment, day programs or workshops after high school require some advance planning. Ask about opportunities and support in your area.
People with Down syndrome can live fulfilling lives. Most people with Down syndrome live with their families, in supported living settings or independently. With needed support, most people with Down syndrome go to mainstream schools, read and write, make decisions, have friends, enjoy an active social life, and have jobs.